Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC: NTC) thermistor is a type of thermistor whose resistance value decreases with increasing temperature and increases with decreasing temperature. The change in resistance value can be caused by the self heating of components caused by external environmental temperature or current in the circuit. The predictability of the resistance value with temperature change is the basis for the application of thermistors.
Negative temperature coefficient thermistors belong to a type of semiconductor components, usually sintered from metal oxides such as manganese, cobalt, nickel, copper, and iron as the main materials, forming different shapes and sizes after sintering. By changing the composition and bulk size of elements in semiconductors, the range of NTC thermistors at room temperature ranges from 1 Ω to 1000000 Ω, with a temperature coefficient of -2% to -6.5%/℃
Diagram of NTC thermistor characteristics: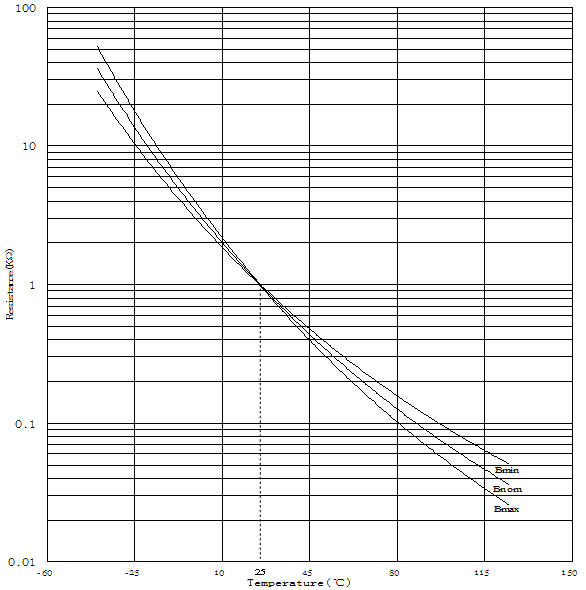
Terminology Description
NTC thermistor
NTC thermistor is a semiconductor component whose resistance value is extremely sensitive to temperature. It is sintered from oxides such as manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), carbon monoxide (Co), copper (Cu), etc. Its main characteristic is that the resistance value changes with temperature.
■ Negative temperature coefficient(NTC)Thermistor
Negative temperature coefficient(NTC)A thermistor is a type of thermistor whose resistance decreases with increasing temperature and increases with decreasing temperature.
■ Zero power resistor(RT)
Zero power resistance is achieved under certain temperature conditions,NTCThe change in resistance value of a thermistor is less than due to the heat generated during measurement0.1%When, this resistance value is called zero power resistance.
■ Rated zero power resistance(R25)
Rated zero power resistance, unless otherwise specified, refers to the resistance at25The resistance value measured in an ambient temperature of ℃。
■ Bvalue
The thermal sensitivity index of resistance value with temperature variation is expressed by the following formula:
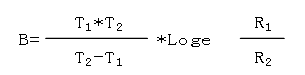
perhaps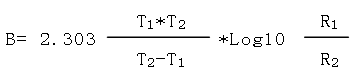
Remarks
B: Unit: Absolute temperature (K)
R1: Resistance value at temperature T1, in Ω
R2: Resistance value at temperature T2, in Ω
T1=298.15K(+25℃),T2=358.15K(+85℃)
The above are the nominal values of T1 and T2. When the specific B value is measured at a certain temperature, T1 and T2 will use the specified value (absolute temperature K) instead of the nominal value during the calculation process.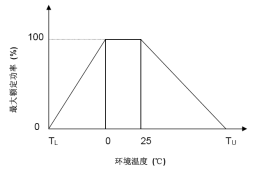
■ Thermal dissipation coefficient(δ)
The thermal dissipation coefficient refers to the specific ambient temperature conditions in a specific medium,NTCThe ratio of the change in power consumption of a thermistor to the change in body temperature is generally usedW/KRepresent.
■ Thermal constant(τ)
Under zero power conditions, when the surrounding temperature changes in a stepped number, the change in the body temperature reaches the difference between its initial temperature and the final temperature63.2%The time required. unit:second(Sec)。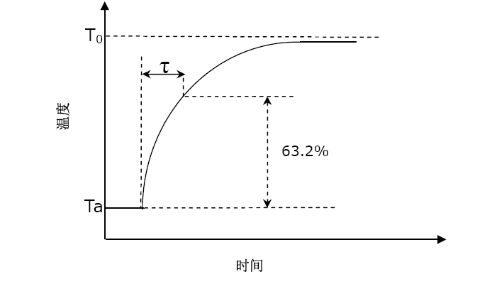
Appendix: Relationship between Thermal Time Constant and Temperature Change Rate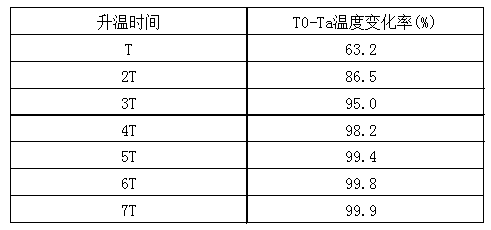
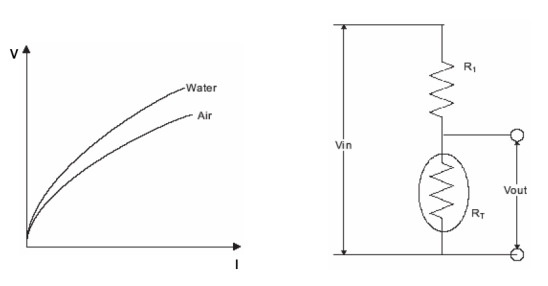
■ voltage-Current characteristics
stay25℃In still air or under specified temperature conditions, addNTCThe relationship between the DC or AC voltage at both ends of a thermistor and the steady-state current passing through it.
■ resistance-temperature characteristic (R-T)
NTCThe relationship between the zero power resistance of a thermistor and its body temperature is approximately calculated using the following formula: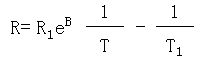
hereRandR1They are respectively at the surrounding temperatureTandT1The zero power resistance value measured under certain conditions, where temperature is expressed in absolute temperature(K)expressK=273.15+℃,BValue is the thermal sensitivity index。
Application Description
■ temperature measurement
NTCThermistors provide practical and low-cost solutions for many temperature measurements, the most common of which is the circuit used for temperature measurementNTCThe circuit for temperature measurement using a thermistor can be composed of a Wheatstone bridge, in which one bridge arm contains aNTCThermistor。
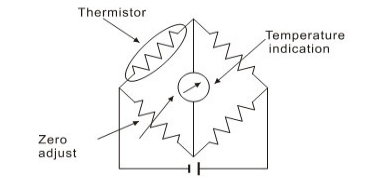
■ temperature control
NTCAs the most sensitive temperature sensing element, thermistors are widely used in temperature control systems. The following diagram is the basic temperature control principle diagram composed of a combination of thermistors and voltage comparators. This circuit can directly convert temperature signals into high and low voltage output signals of the comparator. By using the output voltage of the comparator and appropriate switching elements such as transistors to conduct or cut off the main circuit power supply, temperature control or over temperature protection can be achieved.
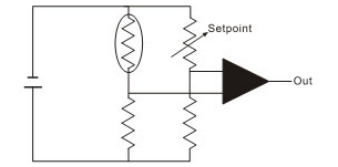
■ temperature compensation
Many semiconductors andICsThere is a temperature coefficient and temperature compensation is required to achieve stable performance over a large temperature rangeNTCThermistors have a high temperature coefficient, so they are widely used in temperature compensation.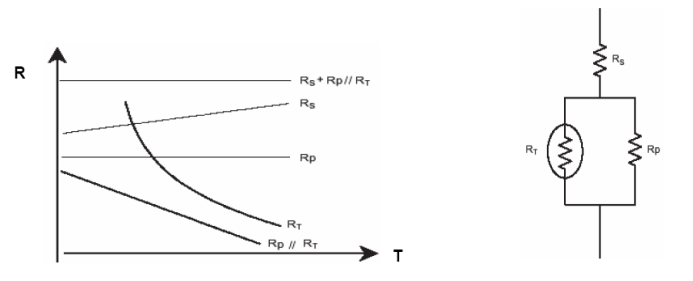
■ Surge current suppression
In electronic circuits containing capacitors, light bulb filaments, fluorescent lamp inverters, and heaters, a surge current that is hundreds of times higher than normal operating current is generated at the moment of switch closureNTCThe zero power resistance value of the thermistor is used to suppress the surge current at the moment of startup, which can prevent the surge current from being too large. After completing the suppression of the surge current, due to the continuous effect of the current passing through it, as the temperature of the thermistor body increases, its resistance value will decrease to a very small extent. The power consumption can be ignored, and the voltage is almost always added to the subsequent equipment to ensure the normal operation of the circuit。
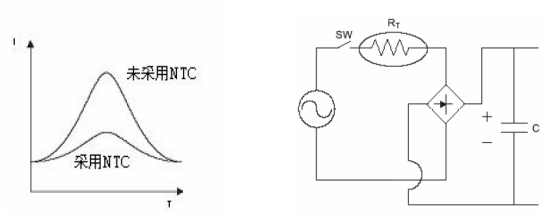
■ Liquid level sensing
Liquid level sensing mainly utilizes the different characteristics of the dissipation constant of a thermistor in liquid compared to air or steam. When the thermistor is immersed in liquid, its dissipation constant will increase, the temperature will decrease, and the voltage at both ends of the thermistor will rise. utilizeNTCThe characteristic of thermistors can accurately detect the presence or absence of liquid at a certain location.
Website Navigation:

Contact person: Miss Li
Mobile number: 13924669192
Phone: 0755-86092836 86094645
Fax: 0755-86092848
Website: korneliadengel.com
Email: szshay@korneliadengel.com
Address: No. 8 Xiangxing Road, Buchong Community, Shajing Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen
Hunan Xinshangying Electronic Technology Co., Ltd
Phone: 0730-2951782
Fax: 0730-2951780
Website: korneliadengel.com
Email: szshay@korneliadengel.com
Factory address: Shangying Industrial Park, No. 8 Changhu Road, Chenglingji Xingang District, Yueyang City, Hunan Province